We always hear the word valuation when it comes to investing properties particularly in subsale. So what is this property valuation anyway?
In this article I will share the purpose, the elements, processes and typical content in a valuation report.
Property valuation can be defined as a process of estimating property value for a certain purpose, at a certain time based on the property’s characteristics by taking into account all the factors that can affect property value. This is done by a professional licensed property valuer to estimate property value.
Discover more topics via spotify. Discover more topics via Spotify
The Purpose of Valuation
Property valuation is carried out for several purposes which can be divided into two main categories namely statutory and non-statutory valuation. Statutory valuation includes all those valuation for the purposes of stamp duty, Property Gains Tax, compensation, and rating. Non statutory valuation includes all those valuation for the purposes of selling and buying, leasing, mortgage and fire insurance. In this article, we are going to focus in non-statutory valuation.
Find out if now is the right time to buy property here.
Property valuation is a complex process and not many investors fully understood how the valuer come into conclusion for any given value.
Property is generally transacted at its market value. This is the amount a property would fetch if offered for sale in the open market at the date of valuation under circumstances that meet the requirements of the Market Value definition.
The market value defined by BOVAEA (Malaysia Board of Valuers, Appraisers and Estate Agents Malaysia) as follow:
Market Value is the estimated amount for which a property should exchange on the date of valuation between a willing buyer and a willing seller in an arm’s-length transaction after proper marketing wherein the parties had each acted knowledgeably, prudently and without compulsion.
In summary for the definition above:
- a willing seller and a willing buyer dealing at arms length;
- a reasonable period within which to negotiate the sale (taking into account the nature of the property and the state of the market);
- values will remain static throughout the period of negotiation for sale;
- the property will be freely exposed to the market
A typical purpose for valuation for any subject property is usually for obtaining loans from the banks. There are other purposes e.g. evaluation of personal wealth and asset etc. Though majority people will usually engage valuer for the purpose of getting loans as it is required by the banks for approving loans. Find out professional fee for valuer here.
The Elements in Property Valuation
First we have to understand what makes a property to have its value?
I’ve researched few papers. The easiest to understand is from (Mohd Harith, 1993), which the author explains the following four criteria that said to contribute to the value of a property;
- useful and beneficial;
- lack in supply
- there is an effective demand; and
- can be transacted.
As real property influence a lot by location and therefore property valuation process involves geographic data that consists of spatial and textual data.
The spatial data involved land size and dimension; specific location or position of lot (end, intermediate and comer lot); street name; location of the housing estate; mukim; district; and state.
The textual data needed include type of building, number of bedroom and bathroom; type of construction and building finishes; and building age and state of repairs.
When the buyer or bank appoints a valuer, the valuation process would be as follow:
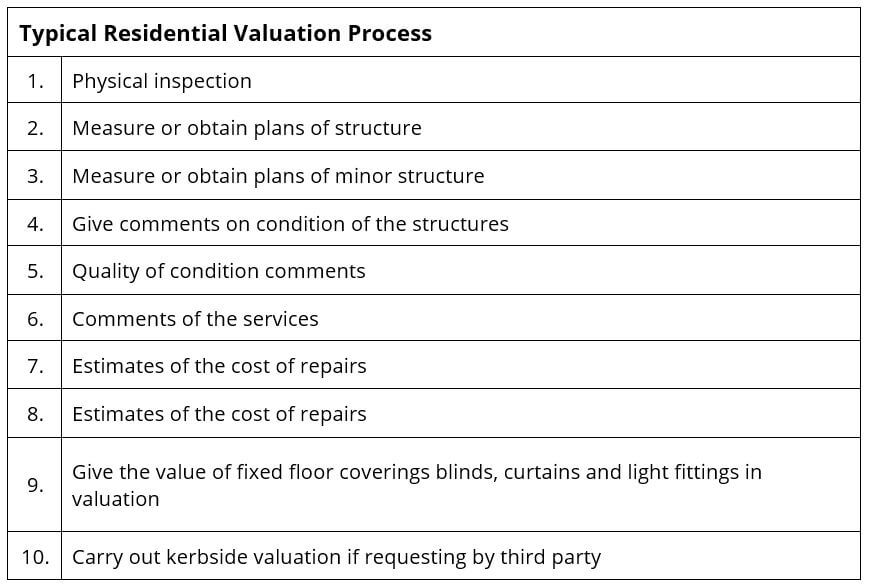
A valuation report is produced upon completion of processes above. The contents in the valuation report will normally include following items:
Subject of valuation
This is subject property that will be assess by the valuer. This includes the address and other information about the property.
Purpose of Valuation
There can be various reasons for valuation. In most cases, it would be for financing as required by the bank prior to granting any loans.
Date of Valuation
Property price changes through time. Thus the time where the valuation is taken place is an important factor to determine whether the value is still valid. Basically valuation report does not carries any expiry date. But ideally, the valuation report is valid after the six months of valuation or maximum one year.
Definition of Valuation
The is the part where the valuer define the definition of a value. It is the written opinion as to capital or rental value on any given basis in respect of an interest in property. This is the part where the valuer define market value and force sale value.
Forced Sale Value is the amount which may reasonably be received from the sale of a property under forced sale conditions which do not meet all the criteria of a normal market transaction.
Particulars of Title
All valuation of any property will include detail information in the title. This include the lot number, size, location, district etc. Any express condition and restrictions imposed on the land will also include in this section.
Location
The exact location of the property with the address will include in this section.
Description of Property
The type of the property along with the layout configuration such as number of rooms and bathrooms is mentioned here. Other information e.g. flooring tiles, kitchen, blinds will be included as well.
Occupancy Status
Occupancy status will check on the rental rate for the unit. If the property is vacant, then the valuer will find similar properties to determine the market rental.
Neighborhood
The surrounding neighborhood around the property.
Services
Any service maintenance fee
Planing
The layout plan of the property
Basis of Valuation
The basis of valuation is the method used to assess the value of a property. Most common approach is Comparison and Income Approach (read more about Income Approach in Valuation here). In valuation for the purpose of bank valuation will usually use Comparison approach as it is more straightforward and easier to compile particularly on the obtaining the data.
In Comparison approach, the valuer must determine the market sales of comparable properties for similar properties. For each of the stated comparables, the minimum information required to be disclosed are the identification of the comparable (usually by way of Lot number and or Title Number), the date of the transaction, the consideration for the transaction, a brief description of the property and the land area. Other information regarding the comparable property that may be provided are analysis in terms of value for the various differences between the comparable property and the subject property.
Evidence of Value
With the comparison approach above, the valuer will need to justify with evidence of transacted property that are similar. A full details for transacted properties including the address, date and value must be included as evidence to support the value.
Valuation
Finally, this is the part where the valuer will give the opinion as to how much the property is worth in the open market.
Conclusion
In my opinion, the valuation report is good if we were to get loans from the banks. However, the reality is that the value doesn’t determine the final price of a property. Price is an amount paid by a buyer to the seller in a property transaction for the exchange of ownership. This means that the market value of a property is not necessarily equivalent to its price. There are many factors that affect the final price of a property. End of the day, it is all about willing buyer and a willing seller. A valuation is just an indication at which price point the negotiation should take place.**
**
If you understood how property valuation works, find out what is Wholesale Real Estate here.